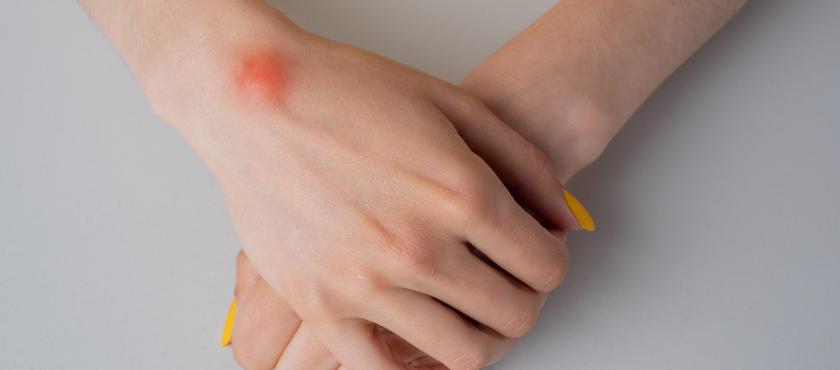
Ganglion cysts are benign growths that most commonly occur in the hands and wrists, although they can be found on the feet as well. They tend to be located by a joint or on a tendon. These growths are located under the skin. They may look rounded or have an irregular shape. They are filled with fluid which can be compared to the natural fluid found in your body that provides joint lubrication. They range in size, from less than 2 mm to 4 cm. They may develop for no apparent reason. Ganglion cysts can disappear without a trace. They can also expand in size, especially when strain is placed on the part of the body where they are found. Repetitive activities often cause them to swell.
What are the Causes of Ganglion Cysts?
There is no definitive answer when it comes to identifying the cause of a ganglion cyst. Many cysts appear without explanation. They form when fluid accumulates in certain parts of the body in the form of a lump that is typically firm. However, they can feel soft as well. In some cases, medical experts can find a root cause for a ganglion cyst, such as:
- Overuse of one part of the body, especially a joint in the hands or feet
- A blow to the affected part of the body
- An injury that affects the joints in the hands or feet
While women are more prone to developing a ganglion cyst, they can also affect men. Athletes that place a great deal of strain on their feet or their hands and wrists are at greater risk of developing a ganglion cyst. They can also develop for anyone who performs a job that places strain on these high-risk parts of the body.
What are Signs and Symptoms of Ganglion Cysts?
Ganglion cysts often cause no symptoms except for the development of an unexplained lump on the hands, wrists, or feet. Typically, only one cyst will appear. In some cases, there may be several that are believed to be connected beneath the surface. If these growths are larger or they are located directly over a nerve, the following symptoms may occur:
- It may be difficult to move the hand, fingers, wrist, or foot in the affected area
- There may be numbness or a tingling when the cyst applies pressure to a nerve
- The area around the cyst may be tender or painful
Smaller ganglion cysts, or cysts that disappear, tend to be less of a problem. Cysts that are larger or swell from an injury or strain could be more bothersome.
What are Treatment Methods for Ganglion Cysts?
In most cases, treatment is not recommended for a ganglion cyst. A doctor may recommend using a splint or brace if the growth is causing difficulties with mobility, numbness, or discomfort. Once the affected area has been immobilized and is no longer placed under any strain, the ganglion cyst may get smaller or disappear. If immobilization does not provide relief, other alternatives may be advised. Aspiration is a minimally invasive procedure in which a doctor will insert a needle into the cyst in order to remove the fluid. While aspiration can reduce the swelling at the time, ganglion cysts often make a return appearance. Surgery is the most invasive option. It is often recommended as a last resort when other options have failed. Surgical removal of a ganglion cyst is an outpatient procedure. The affected area will be numbed through use of a local numbing agent. The surgeon will carefully remove the ganglion cyst. In addition, the stalk, which is the point where a ganglion cyst forms an attachment to connective tissue, will also be removed. In most cases, surgical removal of a ganglion cyst provides a permanent solution. Future ganglion cysts may be avoided in the future by wearing a brace when performing activities that place strain on the affected area. Otherwise, taking action when a cyst first occurs can prevent pain or swelling. Applying a warm compress at the initial appearance of a ganglion cyst may be helpful in accelerating drainage of the fluid that has accumulated.